Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kamiya, Junichiro; Kinsho, Michikazu; Abe, Kazuhiko*; Higa, Kyusaku*; Koizumi, Oji*
Journal of Vacuum Science and Technology A, 36(3), p.03E106_1 - 03E106_10, 2018/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Materials Science, Coatings & Films)The 3 GeV Rapid Cycling Synchrotron (RCS) in J-PARC aims to generate one of the highest power protons in the world, whose design extraction beam power is 1 MW. Beam pipes of alumina ceramics are used to prevent the induced current, which is caused by the rapid change of the magnetic field. In the beam injection section, ceramics beam pipes for a quadrupole magnet and a horizontal shift bump magnet are connected without bellows due to the very limited space. To improve maintainability, the ceramics beam pipes for the quadrupole magnet were newly designed to insert the bellows. We will report the design concept of the new alumina ceramics beam pipes with low spring constant bellows and the several results of the verification tests.
 pressure dependence of SiO
pressure dependence of SiO /Si interfacial oxidation rate studied by real-time photoelectron spectroscopy
/Si interfacial oxidation rate studied by real-time photoelectron spectroscopyOgawa, Shuichi*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Ishizuka, Shinji*; Takakuwa, Yuji*
no journal, ,
In this study, the increased O pressure dependence of the interface oxidation rate was investigated using real-tile photoelectron spectroscopy. The experiment was performed using the surface reaction analysis apparatus placed at the BL23SU of SPring-8. From
pressure dependence of the interface oxidation rate was investigated using real-tile photoelectron spectroscopy. The experiment was performed using the surface reaction analysis apparatus placed at the BL23SU of SPring-8. From 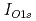 , we can estimate the completion of surface oxidation as 3200 s. Then, O
, we can estimate the completion of surface oxidation as 3200 s. Then, O pressure is increased, and then the interface oxidation is enhanced. The P
pressure is increased, and then the interface oxidation is enhanced. The P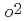 dependence of the interfacial oxidation rate shows that O
dependence of the interfacial oxidation rate shows that O pressure increase makes the interfacial oxidation rate fast, and the interface oxidation rate is proportional to the square root of
pressure increase makes the interfacial oxidation rate fast, and the interface oxidation rate is proportional to the square root of 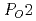 .
.
Sekihata, Yuki*; Ogawa, Shuichi*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Taga, Ryo*; Ishizuka, Shinji*; Takakuwa, Yuji*
no journal, ,
In this study, we investigated the oxidation reaction kinetics on p- and n-type Si surfaces using real-time ultraviolet photoelectron spectroscopy. In the room temperature oxidation, it is found that oxidation reaction coefficient on n-Si(001) is larger than that on p-Si(001). The work function of the n-Si(001) surface shows negative value but p-Si(001) is positive value. From this result, we can estimate the adsorption positions of O atoms. O atoms have a negative charge in the bond of Si-O, so it can be assumed that oxygen is placed on the n-Si(001) surfaces, but it is subsurface in case of the p-Si(001) surface. In case of n-Si(001) substrates, the doped electrons spill out into the surface because many electrons exist in the substrate. As the result, oxidation reaction is promoted in the n-Si(001) surface. From these results, we found that there is a difference of oxidation kinetics depending on the conductivity.